Explore sidecar endpoints
The Substrate sidecar service provides a REST API for interacting with Substrate blockchain nodes built using FRAME. The sidecar REST service exposes an extensive set of endpoints that enable you to interact with nodes, accounts, transactions, parachains, and many other components of a Substrate-based blockchain.
For this tutorial, you'll use Postman to explore the sidecar service.
Postman is a popular platform for inspecting, building, and testing application programming interfaces.
Postman provides an easy-to-use interface that enables both new and experienced API developers to collaborate and experiment using either a browser-based or desktop client.
You'll use a predefined API collection to explore the features sidecar provides through RESTful endpoints.
The predefined API collection provides a set of saved requests created using Postman that you can customize and reuse.
By using API collections that are created with Postman, you have access to features such as inline documentation, reusable variables to access data, error detection in parameter formation, and more.
Before you begin
Before you begin, verify the following:
- You've completed the Quick Start and have the Substrate node template installed and running locally.
- You have Node.js, version 14 or later, available on your local computer to download and install the
sidecarpackage. - You have, or can create, a Postman account.
- You have access to, or can install, the Postman for Web or Postman for Mac client.
Tutorial objectives
By completing this tutorial, you'll learn how to explore the sidecar API REST service using Postman, including how to:
- Download and install the
sidecarservice. - Import a Postman API collection.
- Set up a working environment.
- Make API requests to the
sidecarAPI. - Save the data for further use.
Download and install sidecar
To download and install sidecar:
- Open a terminal shell.
-
Install the
@substrate/api-sidecarservice globally or locally usingnpmoryarn.For example, if you use
yarn, run the following command for global installation of the@substrate/api-sidecarservice:yarn global add @substrate/api-sidecarIf you use
npmas your package manager, run the following command for global installation of the@substrate/api-sidecarservice:npm install -g @substrate/api-sidecar -
Verify you have a Substrate node running for the service to connect to.
By default, the service attempts to connect to the local host using ws://127.0.0.1:9944. You can configure the service to use a different URL by modifying the SASSUBSTRATEURL environment setting. If you want to connect to the node template running locally using the default port, not configuration is necessary.
-
Start the service by running the following command:
substrate-api-sidecarIf you are using the default configuration, you should see output similar to the following:
SAS: 📦 LOG: ✅ LEVEL: "info" ✅ JSON: false ✅ FILTER_RPC: false ✅ STRIP_ANSI: false 📦 SUBSTRATE: ✅ URL: "ws://127.0.0.1:9944" ✅ TYPES_BUNDLE: undefined ✅ TYPES_CHAIN: undefined ✅ TYPES_SPEC: undefined ✅ TYPES: undefined 📦 EXPRESS: ✅ BIND_HOST: "127.0.0.1" ✅ PORT: 8080 2023-01-04 14:35:41 info: Version: 14.2.2 2023-01-04 14:35:41 warn: API/INIT: RPC methods not decorated: transaction_unstable_submitAndWatch, transaction_unstable_unwatch 2023-01-04 14:35:41 info: Connected to chain Development on the node-template client at ws://127.0.0.1:9944 2023-01-04 14:35:41 info: Listening on http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 2023-01-04 14:35:41 info: Check the root endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:8080/) to see the available endpoints for the current node
Import the API collection
To use the predefined API collection for sidecar:
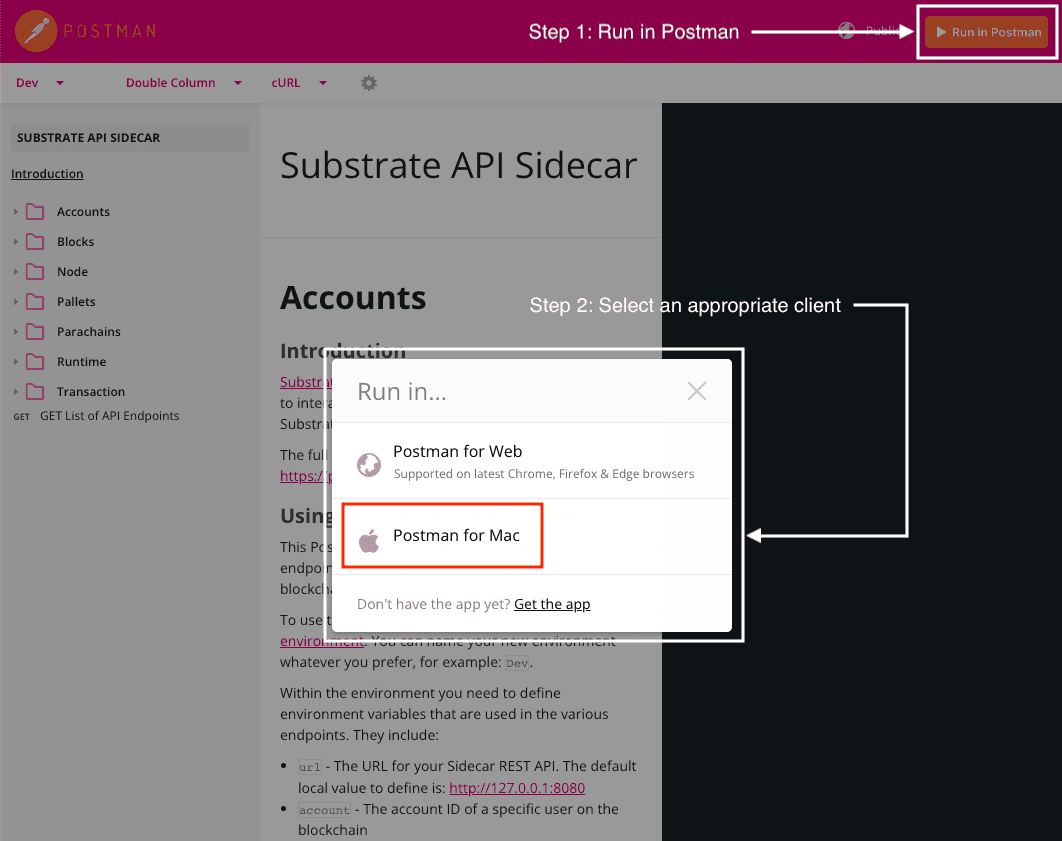
- Open the predefined Substrate API Sidecar API collection in a browser.
- Click Run in Postman in the top-right corner of the page.
-
Select to run the collection either using Postman for Web or in the Postman for Mac desktop client.
In you are using a macOS computer, you should run the collection with the desktop client because the desktop client is generally more stable and supports more features. If you don't have Postman for Mac installed on your local computer, click Get the app to download it.
![Run the API collection in Postman]()
-
Select a workspace in Postman, then click Import to add the predefined collection to your Postman workspace.
After you open the Substrate API
sidecarcollection in Postman, you are ready to start defining your environment variables.
Define environment variables
The predefined Postman API Collection comes with a built-in development environment named Dev.
This environment includes the predefined variables for you to use in the different API requests to the sidecar service using the predefined queries.
The variables defined in the Dev environment include the following:
urlto specify the URL for yoursidecarREST API to use. The default value ishttp://127.0.0.1:8080.accountto specify the account identifier of a specific user on the blockchain.numberto specify the number of a specific block from the blockchain.extrensicIndexto specify the index number of a specific extrinsic in a block.assetIdto specify the identifier of a pallet asset.storageItemIdto specify the identifier of a pallet storage item.paraIdto specify the unique numeric identifier for a specific parachain.
All requests require the url variable.
The Dev environment provides http://127.0.0.1:8080 as the default value for the url because that URL is the default REST API address created when you start a new instance of the sidecar service.
If you have set the sidecar service to use an external hosting location or changed the default local URL using an environment setting, you must change the default value for the url variable accordingly.
In addition to the url variable, different types of requests require you to define different variables.
For example, in this tutorial, the query to return the balance of a specific account on the blockchain requires you to define a value for the account variable.
Get a list of endpoints
You can use Postman to send a GET request to sidecar to return a list of all the active endpoints available for the API collection.
This request requires only the url variable to be defined.
In most cases, you can use the default value for the local host IP address and port unless you are using sidecar outside of the local development environment.
To get a list of endpoints:
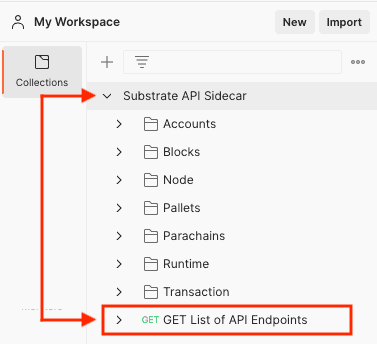
- In the Postman client, click Collections and open the Substrate API Sidecar collection.
-
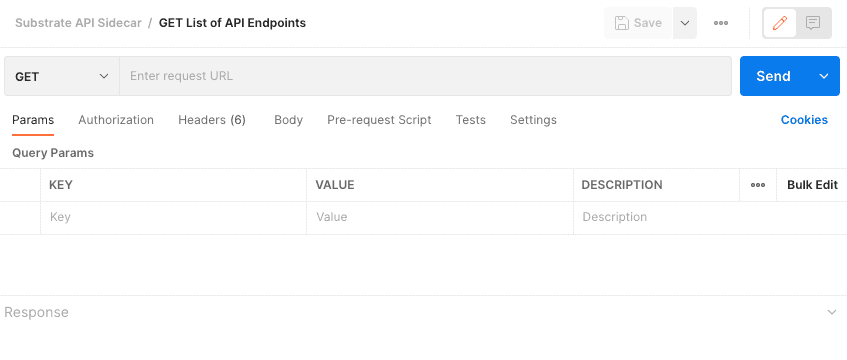
From the list, select the GET List of API Endpoints request.
![Select the GET Endpoints request]()
After you select the Get the List of API Endpoints request, Postman displays the options available for this request. Because this request only requires the URL and doesn't use any other parameters, there are no settings to configure here.
![Set parameters for the request]()
If a request takes additional parameters, you can experiment by providing different values for the parameters and seeing how those values provide different responses from the API.
-
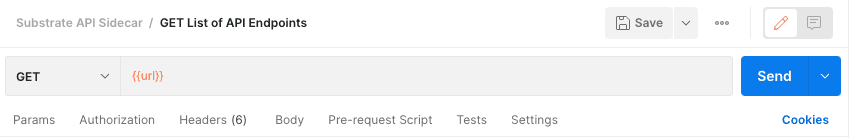
Specify the URL to connect to using the predefined
urlvariable by typing{{url}}.![Specify the URL for the request]()
-
Click Send.
After you send the request, you should see the response section in Postman populated with data. By default, the data is displayed in JSON format, but you can change response to XML, HTML, or plain text. You should see information similar to the following partial response:
{ "docs": "https://paritytech.github.io/substrate-api-sidecar/dist", "github": "https://github.com/paritytech/substrate-api-sidecar", "version": "14.2.2", "listen": "127.0.0.1:8080", "routes": [ { "path": "/accounts/:address/asset-balances", "method": "get" }, { "path": "/accounts/:address/asset-approvals", "method": "get" }, ] } -
Click Save response to save this response to an output file if you want to use it to build features for your own applications.
You can also save the response as a example for future reference. If you save the response as an example, it is added underneath the GET List of API Endpoints request option.
This list of endpoints request is a useful demonstration of a simple request. However, more often, you'll want to use sidecar endpoints to access specific data that will require you to manipulate the values defined for different variable to retrieve the specific information you want.
That's the next step in this tutorial.
Get account information
Now that you are familiar with making an uncomplicated request, let's perform another GET request but this time modifying the value of one of the environment variables.
In this request, you'll request the balance for a specific account on the chain.
Using the substrate node template as the working blockchain, this request queries the account balance of the Alice user.
To get account information for the Alice address:
- Open a new terminal shell.
-
Copy the account address for Alice.
For example, inspect key information for the
//Aliceaccount by running the following command:./target/release/node-template key inspect //AliceCopy the public key for the account:
5GrwvaEF5zXb26Fz9rcQpDWS57CtERHpNehXCPcNoHGKutQY -
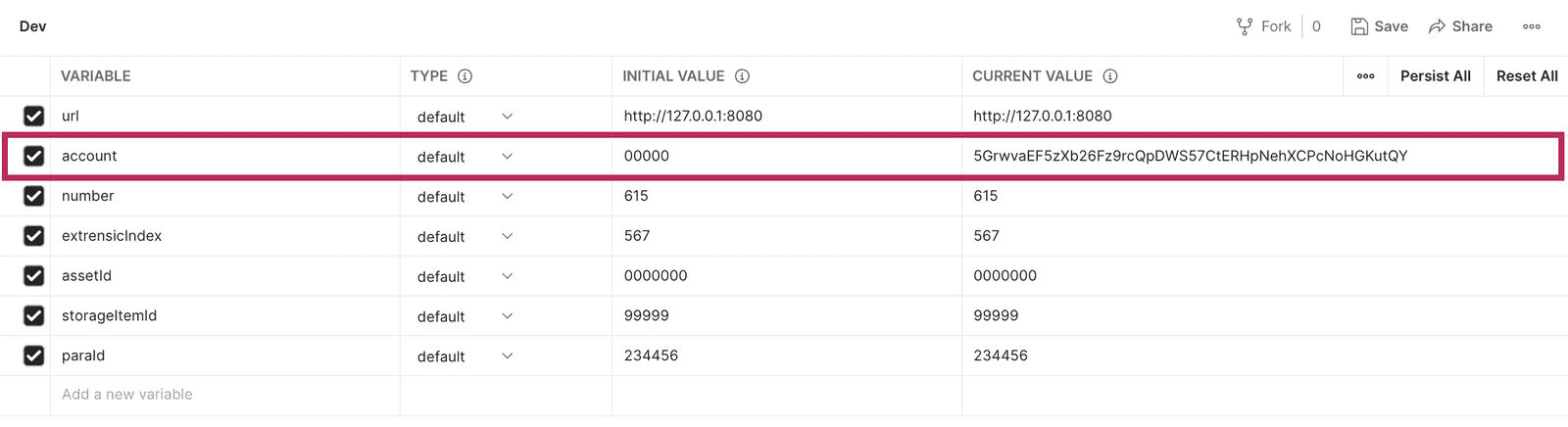
In the Postman client, select the Dev environment to display the list of environment variables and their values.
For each variable, there's an initial value and a current value.
- The
initial valueis what the variable is loaded with when starting a freshDevenvironment. - The
current valueis the value for the current session.
The
current valueis only saved locally and never sent to Postman or shared with other team members using the same Postman API collection. - The
-
Paste the account address for
Aliceinto thecurrent valuefield.![Account variable in Postman environment]()
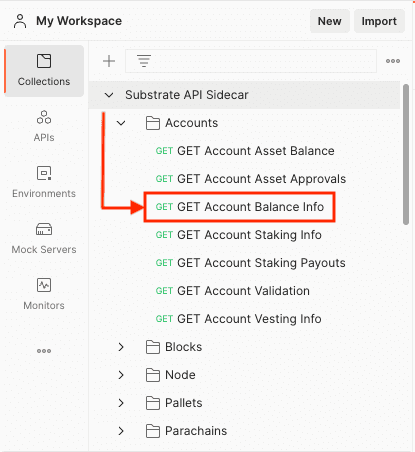
- Click Collections and open the Substrate API Sidecar collection.
-
Select the Accounts folder, then select GET Account Balance Info.
![Select the Account Balance Info request]()
-
Configure the request using the
urlvariable that you used previously and theaccountvariable you set in Step 4:![Specify the endpoint for the request]()
-
Click Send.
You should receive a response that looks similar to the following in JSON format:
{ "at": { "hash": "0xfc354903a665c7847ba4f83dd9e5fb0389e31bc2015086aca56a68bb345493a5", "height": "1189" }, "nonce": "0", "tokenSymbol": "UNIT", "free": "1152921504606846976", "reserved": "0", "miscFrozen": "0", "feeFrozen": "0", "locks": [] }
You can save this response as a file or as an example within Postman to assist you in creating tests or building your own applications.
What's next?
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Import an API collection into Postman.
- Define environment variables to use in a collection.
- Send API requests with custom variable definitions.
- Inspect and save the responses from the API.
You now have a good working basis for using sidecar endpoints within Postman and to begin building applications that use the sidecar API for your own purpose.
To explore more on your own, consider the following tasks:
- Send requests using the other endpoints in the predefined collection.
- Write tests in Postman for debugging purposes.
- Set up Postman flows that allow you to connect a series of API REST requests.